What is Antiperspirant?
Antiperspirant is a personal hygiene product designed to control sweating by clogging the armpit sweat glands. It comes in aerosol sprays, sticks, creams, gel, roll-on or solid sticks.
The History of Antiperspirant
Deodorant and antiperspirant have been used for thousands of years in various forms. Aluminum crystals, a crude, raw type of antiperspirant, were found in Egyptian pharaoh tombs.
Before modern-day antiperspirants, people also battled body odor by dousing themselves in perfumes between regular washings.
The first modern antiperspirant was Everdry. Launched in 1903, Everdry used aluminum salts to block pores and stop sweating, but early versions caused skin irritation and didn't catch on.
A few years later, a surgeon invented a liquid antiperspirant to keep his hands from sweating while operating. His daughter tried it on her armpits and found it stopped body odor and sweat. She started selling it, marking the beginning of the antiperspirant we know today.

How Does Antiperspirant Work?
To understand antiperspirant and choose the right sweat protection, you need to know how it works.
Sweat & Antiperspirant
Sweat regulates your body temperature, so you don't overheat. It's a crucial body function, but sometimes our body sweats more than needed (ever experience sweat stains or stress sweating?)
That's where antiperspirant comes in.
There are two types of sweat glands on your body. Eccrine sweat glands are located all over your body. Apocrine sweat glands appear by your hair follicles, mainly concentrated in your scalp, armpits and groin.

Bacteria thrive in the warm, moist environments where your apocrine sweat glands are located, which is why you experience odor in your armpits and groin area. Even though your sweat is odorless, body odor occurs when sweat interacts with bacteria on your skin.
Antiperspirant targets the smelly apocrine sweat glands. Aluminum (the active ingredient in antiperspirant) dissolves onto your skin's surface to form a gel. The gel temporarily plugs your apocrine sweat glands to reduce sweating.
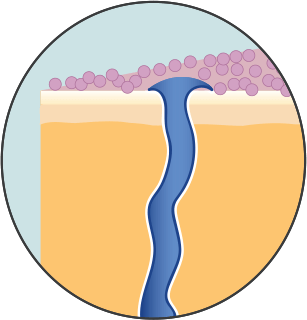
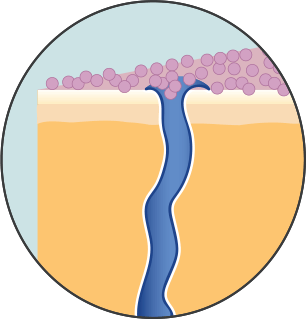
Deodorant only prevents body odor. It doesn't control or stop sweating.
So What Does Deodorant Do?
Soap and water aren't 100 percent effective at killing bacteria — which is why most people also wear deodorant or antiperspirant. But did you know there's a difference between the two?
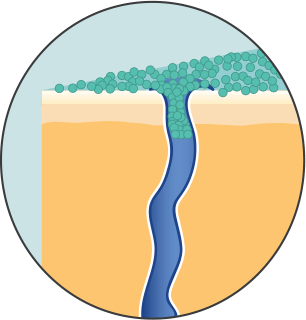
Deodorant only prevents body odor. It doesn't or stop sweating. Deodorants are mostly alcohol-based, made of compounds like sodium chloride and stearyl alcohol.
Some deodorants also contain antimicrobials like triclosan that stop bacterial growth in your underarms. Preventing bacteria growth prevents body odor — however, it doesn't reduce the amount of sweat that comes out of your pores like antiperspirant.
When to Use Deodorant vs. Antiperspirant
Now that you know the difference between deodorant and antiperspirant, how do you know which one to use?
It depends on how much you sweat. Here are a few different sweating scenarios:
Should I Use Deodorant or Antiperspirant?
- You sweat constantly.
- You need to prevent wet marks.
- You sweat heavily or have hyperhidrosis.
- For nerve-wracking situations, like a first date or job presentation.
Best Solution: Antiperspirant
If want to avoid wet marks and reduce how much you sweat, look for an antiperspirant.
- You need something to combat the B.O.
- You want to go with the natural route and avoid chemicals.
- You just want to smell fresh.
- You have sensitive skin.
Best Solution: Deodorant
If B.O. is the main culprit, deodorant is the best option.
Side Effects of Antiperspirant
Antiperspirant is potent. Because it actively blocks sweating (a biological, natural body function), it's labeled as a drug by the FDA.
However, there's also a lot of confusion and misinformation regarding antiperspirant side effects.
Is Antiperspirant Bad For You?
Antiperspirant has stirred a lot of controversy and questions in recent years, specifically around side effects and its relationship to breast cancer and tumors.
The concerns stem from the use of aluminum, the active ingredient in antiperspirant.
Antiperspirant and Cancer
One of the top concerns is the link between antiperspirant and breast cancer.
A few studies theorize that using antiperspirants increases your chance of getting breast cancer. Because you apply antiperspirants near the breast, some researchers were concerned about a possible connection between antiperspirant and breast cancer.
But many of the studies that ignited the hype were flawed from the beginning. Countless experts and studies, including the National Cancer Institute, found no evidence that linked antiperspirants to breast cancer.
Antiperspirant and Parabens
Parabens are another commonly cited concern. Parabens are preservatives typically used in deodorants and antiperspirants. They mimic estrogen in the body and have been reportedly found in breast tumors.
However, scientific evidence doesn't support this claim, and most deodorants and antiperspirants no longer contain parabens.
How to Use Antiperspirant
Yes, antiperspirant can help you sweat less — but that doesn't mean you should go crazy. Side effects can happen, especially if it's not applied correctly. Overuse can irritate sensitive skin and even cause rashes and redness.
When using antiperspirant, make sure to follow these tips to avoid any side effects:
- Follow instructions carefully: Many antiperspirants need to be applied the night before for maximum effectiveness.
- Use an emollient or moisturizer: Using a moisturizer can prevent skin irritation. (You can also look for antiperspirants that contain moisturizer.)
- Start small: Don't go immediately for the prescription or clinical-strength antiperspirant. Start slow, see how your skin reacts and find the one that works for you.



